SEO is not what it was a few years ago. If you’re feeling like the search landscape in 2025 is a whole new world, you’re not alone. As an SEO and web performance specialist, I’ve watched search engines evolve and user habits shift. The good news is that by focusing on the right strategies, you can stay visible online even as voice assistants answer questions and AI tools summarize content. In this article, we’ll dive into what’s working now – from understanding user intent and mobile-first best practices to technical SEO fundamentals, Core Web Vitals, long-tail voice queries, and building E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness). Let’s get into the practical steps you can take to boost your visibility in 2025’s AI-driven search results.
Putting User Search Intent First
One of the biggest shifts in SEO is the emphasis on search intent. In the past, you might have targeted a short keyword and hoped for the best. Today, it’s crucial to think about why someone is searching and what format of content will best satisfy them. Google has become very good at understanding context and intent – for example, telling if a user is just researching a topic or is ready to make a purchase. SEO in 2025 is therefore more intent-focused than ever.
What does this mean for you? It means your content strategy should revolve around providing exactly what the searcher needs:
-
Match content to intent: Figure out if the queries you target are informational (seeking knowledge), navigational (seeking a specific site), transactional (looking to buy something), or commercial investigation (comparing options). For an informational query, a comprehensive how-to guide or blog post works best. For a transactional query, a product page or service page optimized to convert is more appropriate.
-
Address the user’s questions: Within your content, directly answer common questions users have. Google’s “People also ask” suggestions can hint at what people expect to learn. By covering those questions in your article (perhaps as subheadings or an FAQ section), you increase the chance of satisfying the search intent and appearing for related queries.
-
Think in topics, not just keywords: The days of one page per keyword are gone. Now it’s about creating clusters of content that cover a broad topic and all its subtopics. This not only signals to search engines that you comprehensively answer a searcher’s needs, but also keeps users engaged by guiding them through their learning or buying journey. In practice, this could mean writing a pillar page for “email marketing” and supporting pages for “email marketing best practices,” “email automation tools,” etc., all interlinked logically.
By aligning your content with user intent, you provide real value. Not only will Google “rank helpful and reliable websites” higher, but visitors will stay on your site longer and be more likely to convert since they’re finding exactly what they came for.
Adapting to AI-Driven Search Results
Another game-changer in 2025 is the rise of AI-generated search results and answer engines. If you’ve searched on Google lately, you’ve probably noticed AI-powered summaries or answer boxes at the top of the results. These are often referred to as AI overviews – they pull information from various websites to give the user an immediate answer. In other words, search engines are increasingly becoming answer providers, not just link providers.
For website owners and SEOs, AI-driven SERPs (Search Engine Results Pages) have a clear impact: some users get their answer without ever clicking through. While that sounds scary, it doesn’t mean SEO is dead – but it does mean we have to adapt our content strategy to earn and maintain visibility in these new results formats.
Here are strategies to stay visible when search engines themselves are generating answers:
-
Structure content in a Q&A format: Organize portions of your content around key questions and answers. Use clear headings phrased as questions, and immediately follow with a concise answer. This approach makes it easier for Google or Bing’s AI to grab your content for a featured snippet or overview. Content that’s structured with FAQs or explicit Q&A sections stands a better chance of being highlighted in an answer box.
-
Provide concise, valuable answers up front: Aim to answer the question in the first 40–60 words after the question heading. Think of this as the “summary” or snippet that could appear on the SERP. Get to the point quickly and accurately, while implying there’s more to learn if the user clicks through.
-
Use lists, tables, and structured data: When appropriate, format information as bullet points, numbered steps, or tables. Structured information is both user-friendly and favored by search engines for rich results. A step-by-step list or comparison table can increase your chances of being featured.
-
Include authoritative facts and sources: If you present a statistic or claim, back it up with a reputable source (and link to it). The more trustworthy your content, the more likely it will be featured in AI-generated summaries.
The goal is to win the snippet or AI summary spot, but also to entice users to click through. Strike a balance: answer the question directly, but hint at deeper insights. For example:
“Core Web Vitals are a set of user experience metrics (measuring page load speed, interactivity, and stability) that Google uses as a ranking factor – more on these metrics later in the article.”
Lastly, track your presence in these AI-driven elements. Even if a user doesn’t click, being the source of an AI-generated answer builds brand awareness. Use tools like Search Console to monitor impressions in featured snippets or zero-click searches. This helps you identify which content is effective and where to focus next.
Mastering Mobile-First Indexing and Mobile UX
We’re well into the era of mobile-first indexing, where Google predominantly uses your site’s mobile version for crawling and ranking. Why did Google switch to mobile-first? Simply put, the majority of search traffic now comes from mobile devices. In fact, over 60% of organic search visits in the U.S. come from mobile devices, and Google completed its full move to mobile-first indexing in late 2023. In 2025, if your site doesn’t deliver a great mobile experience, your SEO will undoubtedly suffer.
To succeed with mobile-first indexing, make sure you prioritize mobile user experience at every turn. Here are the key considerations:
-
Responsive design: Your site should use a responsive design that adapts to different screen sizes. This ensures all your content, images, and structure are consistent and accessible on mobile. A responsive site prevents scenarios where something important (like a piece of content or a navigation link) is visible on desktop but hidden on mobile. Google will index the mobile view – so everything critical for SEO must be present and user-friendly on mobile.
-
Mobile-friendly navigation: Think about how users interact on a small touchscreen. Buttons and links need to be tap-friendly – sufficiently large and well-spaced so users don’t accidentally click the wrong thing. Simplify your menus and avoid deep, convoluted menu structures. A good rule of thumb is to keep important pages no more than a tap or two away from the homepage on mobile.
-
Readability: Use fonts that are legible on a phone without zooming. The text should automatically resize or wrap so that users never have to scroll side-to-side. If a user has to pinch-to-zoom or turn their phone to read your article, that’s a poor experience (and Google notices that).
-
Performance on mobile networks: Mobile users aren’t always on Wi-Fi; they might be on spotty 3G/4G or congested networks. Optimize your page size and loading sequence so that even on slower connections, the page loads quickly. This includes using optimized images, minifying code, and leveraging browser caching. Fast loading times on mobile are crucial – a page that’s fast on desktop but slow on a phone will hurt your mobile rankings.
-
No mobile-specific errors: Ensure that your mobile version isn’t hiding content behind interstitials or pop-ups. Obtrusive interstitials (like big “download our app” banners) can negatively impact SEO. Also double-check your structured data, metadata, and hreflang tags (if applicable) to be sure they match between mobile and desktop versions.
A quick way to evaluate your mobile readiness is to use Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test or PageSpeed Insights for mobile. These tools will point out issues like clickable elements being too close together or content wider than the screen. Regularly audit your site on a real smartphone (not just emulators) — experience it as your visitors do.
In summary, mobile-first indexing means mobile-first thinking. By delivering a smooth mobile experience, you’re not only aligning with Google’s indexing model but also delighting the majority of your visitors. And happy visitors lead to better engagement signals, which can further boost your SEO.
Technical SEO Hygiene: The Foundation of Visibility
Think of technical SEO as the engine under the hood of your website – if it’s not well-tuned, it doesn’t matter how nice the paint job is. Technical SEO hygiene covers all the behind-the-scenes aspects that help search engines crawl, index, and understand your site (and that help users navigate it without issues). In 2025, maintaining technical SEO best practices is just as critical as ever for sustaining your visibility.
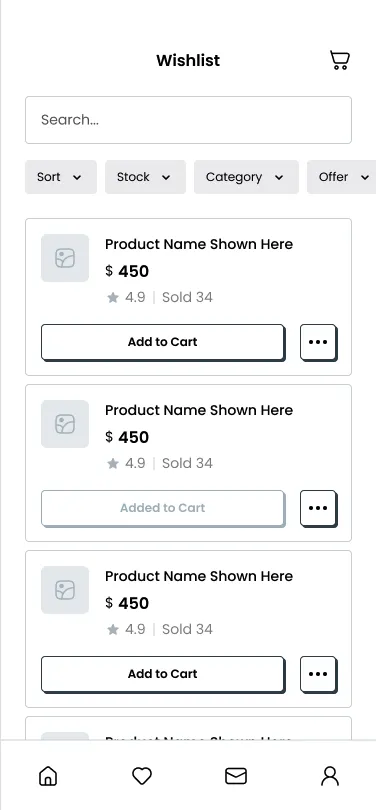
 _Initial audit showing crawl issues, warnings, and opportunities for improvement._
_Initial audit showing crawl issues, warnings, and opportunities for improvement._
I’ve conducted many SEO audits, and it’s common to discover hidden technical issues that hold a site back. Some classic examples of technical problems include:
- Slow page speed: Perhaps your pages are bloated with large images or too many scripts. (We’ll address speed specifically with Core Web Vitals next, but it’s worth noting here that speed issues often fall under technical audits.)
- Broken links: Both internal links and outbound links that lead to 404 errors. Broken links hurt user experience and can disrupt crawling (if your internal link structure has dead ends).
- Missing or duplicate meta tags: Title tags and meta descriptions that are missing, duplicated across pages, or too long/short can hinder your SEO. They might not directly tank your rankings, but they affect click-through rates and how Google understands the relevance of your pages.
- Thin or duplicate content: Having many low-value pages (e.g., nearly empty pages or pages with very similar content) can drag down your site’s overall quality in Google’s eyes. Each page should serve a distinct purpose. This issue often comes to light in technical audits when we crawl the site and see what pages exist.
- Missing alt text on images: Often overlooked, image alt text is important for accessibility and gives search engines context about your images. An audit might reveal dozens of images with no alt attributes, which is a missed opportunity (especially if those images are product photos or infographics that could drive search traffic).
- XML sitemap or robots.txt issues: Sometimes sitemaps contain broken URLs or haven’t been updated to include new content. Or a misconfigured robots.txt file might accidentally block important pages from being crawled.
These kinds of errors are technical SEO 101, but they do happen and can seriously impact your visibility if not fixed.
So, what can you do to maintain good technical SEO hygiene?
- Conduct regular SEO audits: If you have the expertise, use tools (like Screaming Frog, Sitebulb, or Google Search Console) to crawl your site and identify problems. If you prefer a professional touch, consider bringing in an SEO specialist (our team at Thursday Creative offers comprehensive technical audits as part of our Search Engine Performance Optimization services). Aim to audit at least once a year – or more frequently if you run a large, frequently changing site.
- Fix errors methodically: Prioritize issues that directly affect crawling and indexing first (like robots.txt disallowing important pages or major site errors). Next, tackle things that hurt user experience (broken links, slow pages). Then fine-tune the smaller details (like meta tag improvements or schema markup additions). It helps to keep a running log of fixes so you can track improvements.
- Leverage Google Search Console: GSC will alert you to crawl errors, mobile usability issues, indexing problems, and even security issues. For example, if Google can’t index some pages due to a server error or detects mobile usability problems, GSC will let you know. Set up email alerts or check regularly – it’s like a health monitor for your site.
- Stay updated on technical best practices: SEO evolves. Keep an eye on updates from Google (via their Search Central blog) or trusted SEO news sources. For example, Google recently replaced the First Input Delay metric with Interaction to Next Paint in Core Web Vitals. Staying current ensures your efforts align with what search engines prioritize.
Maintaining technical SEO hygiene ensures that all your front-end optimizations – great content, fast performance, rich snippets, etc. – can be fully appreciated by search engines. It’s the bedrock of your SEO efforts. Fixing technical issues might not be glamorous, but it can deliver real results in rankings, traffic, and user satisfaction.
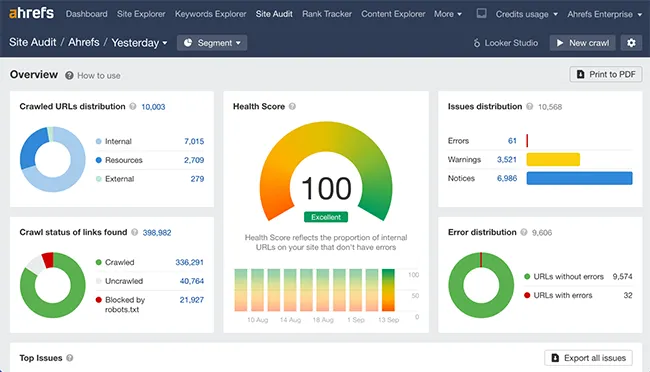 _Post-cleanup: a perfect 100 Health Score in Ahrefs, showing strong technical SEO hygiene._
_Post-cleanup: a perfect 100 Health Score in Ahrefs, showing strong technical SEO hygiene._
Speed and Core Web Vitals: User Experience as a Ranking Factor
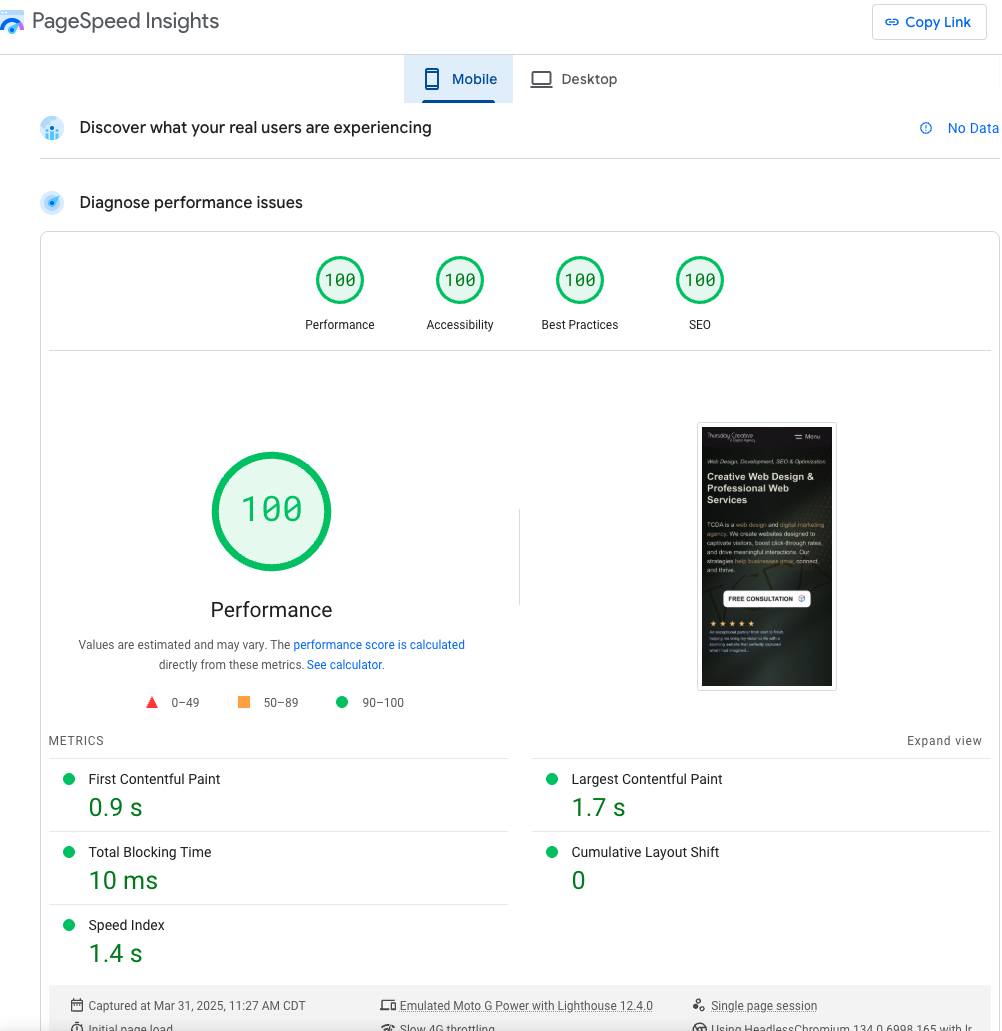
Site speed and user experience have moved from a “nice-to-have” to a “must-have” in SEO. Google has explicitly made page experience part of its ranking considerations in recent years, which includes metrics called Core Web Vitals. Core Web Vitals (CWV) are a set of metrics that measure key aspects of user experience: loading performance, interactivity, and visual stability. As of 2024, they consist of:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): How quickly the main content of the page loads – essentially, the render time of the largest text or image block visible in the viewport. A good LCP is under 2.5 seconds on mobile.
- Interaction to Next Paint (INP): How quickly the page responds to user input. (INP is a newer metric, replacing First Input Delay.) It gauges the responsiveness of your site – when a user clicks a button or link, how soon does the page begin to process that interaction? Lower is better, indicating a more responsive page.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): How stable the page layout is as it loads. If elements are moving around and causing the user to lose their place (for instance, an image loading late and pushing text down, or an ad popping in and shifting content), that’s a high CLS – not good. You want pages to load with minimal unexpected layout shifts.
Google continues to prioritize user experience, and Core Web Vitals remain a crucial factor in search rankings. In plain terms: if your site frustrates users, Google is less likely to rank it highly. Conversely, if your site is fast and smooth, you have a better shot at ranking – all else being equal.
Improving Core Web Vitals can be technical, but here are some actionable steps:
-
Optimize and compress images: Images are often the heaviest elements on a page. Use modern formats like WebP or AVIF to reduce file size without losing quality. Don’t load huge dimensions when smaller ones will do. Optimized images improve LCP directly.
-
Eliminate render-blocking resources: Too many CSS and JavaScript files can delay page rendering. Minify and combine CSS, defer non-critical JS, and remove unnecessary scripts. Reducing unused JavaScript improves both LCP and INP.
-
Implement lazy loading: For images or iframes below the initial viewport, use lazy loading so they only load when the user scrolls to them. This improves initial load time and reduces upfront browser work.
-
Reserve space for content: To avoid layout shifts (CLS), specify size attributes or use CSS aspect ratios for images and videos. This ensures the browser reserves space before media loads. Avoid injecting content above what’s already visible unless it’s controlled and expected.
-
Use a CDN and good hosting: A Content Delivery Network (CDN) serves your site faster from locations near users. Fast hosting improves server response time, which is crucial for good LCP.
-
Self-host fonts: Hosting fonts locally avoids third-party delays and gives you control over performance. Use modern formats like
.woff2and preload important fonts:<link rel="preload" href="/fonts/Inter.woff2" as="font" type="font/woff2" crossorigin="anonymous" /> -
Defer or async JavaScript: Prevent scripts from blocking rendering by using
deferfor scripts that rely on DOM andasyncfor independent scripts like analytics:<script src="/js/main.js" defer></script> <script src="https://example.com/analytics.js" async></script> -
Use code-splitting or lazy loading: Break JavaScript into smaller chunks and load components only when needed. This is often supported by modern build tools like Astro or Vite:
import("./components/Chart.js").then((module) => { module.initChart(); }); -
Inline critical CSS and defer the rest: Deliver only essential styles immediately and load the rest after rendering. I put the css at the end of the page. This improves perceived speed:
<style> p, li { font-size: 1rem; line-height: 1.5rem; font-weight: 300; } img { max-width: 100%; } ul { list-style: none; } .mobile-image { max-width: 350px; width: 70%; } header { display: grid; grid-template-columns: repeat(5, 1fr); } </style> <link rel="stylesheet" href="/styles/global.css" media="print" onload="this.media='all'" /> <noscript><link rel="stylesheet" href="/styles/global.css" /></noscript>
The payoff for improving these metrics is more than just appeasing Google’s algorithm. A fast, stable site also increases conversions and reduces bounce rates. According to research, a site that loads in 1 second converts 3x better than one that loads in 5 seconds.
If you’re unsure about your Core Web Vitals, check the report in Google Search Console. You can also use PageSpeed Insights or Lighthouse for lab data and improvement tips.
In 2025, page experience is a make-or-break factor. Users expect speed and stability. Meeting those expectations is key to both ranking well and keeping people on your site.
Long-Tail Keywords and Voice Search Optimization
With the explosion of voice assistants and natural language queries, voice search has become an integral part of how people find information. In 2025, ignoring voice search means missing out on a growing segment of searches that are often highly specific and intent-rich. Let’s break down why voice and long-tail keywords matter and how to optimize for them.

Voice search adoption is significant. Worldwide, about one in five people are using voice search – that’s hundreds of millions of users asking Siri, Alexa, Google Assistant, or Cortana for quick answers. In the U.S. alone, projections showed over 150 million voice assistant users by 2025. A large portion of voice searches are local in nature (think “Where’s the nearest coffee shop?”). Roughly 22% of voice queries are location-based, and some studies put “near me” voice searches even higher.
Voice queries tend to be longer and more conversational than typed queries. Someone might type “weather Chicago” but ask “What’s the weather in Chicago this weekend?” by voice. These natural language patterns often manifest as long-tail keywords (longer, specific phrases). Long-tail searches might have lower individual search volume, but collectively they account for a huge percentage of overall searches – and they often indicate a user who knows exactly what they want.
To capture voice search traffic (and long-tail traffic in general), consider these strategies:
-
Optimize for conversational language: Review your content and see if it reads like natural speech. Use long-tail keywords that mimic real speech (including question words like who, what, where, when, why, and how). Phrases like “The best time to visit Paris is…” mirror how voice queries are phrased.
-
Leverage FAQ pages and sections: Q&A formatted content is gold for both regular and voice SEO. For example, a plumbing business might include: “How do I fix a leaky faucet?” or “When should I call an emergency plumber?” Clear, concise answers improve your chances of being featured in voice results.
-
Target long-tail keywords in your SEO strategy: Don’t just focus on broad terms. Build content around detailed queries like “best running shoes for flat feet in 2025.” These phrases often have less competition and higher conversion intent.
-
Don’t forget local SEO for voice: Many voice searches are local. Keep your Google Business Profile updated. Include your location and service areas naturally in your content, like “We offer lawn care services throughout Austin, Texas.”
-
Provide context for complex queries: Voice searches can combine multiple criteria. Be explicit about what you offer. If you cater to specific needs or situations, state that clearly on your website so voice assistants can match those details.
Voice search and long-tail SEO go hand in hand. Optimizing for natural language helps your content reach users in conversational search environments — and often improves overall usability and engagement.
E-E-A-T: Building Experience, Expertise, Authority, and Trust
Google’s focus on quality has crystallized into a concept known as E-E-A-T: Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness. This comes from Google’s Search Quality Rater Guidelines. While E-E-A-T itself isn’t a direct ranking factor, it strongly influences how Google evaluates content — especially in competitive or sensitive niches.

Let’s break down what E-E-A-T means and how to improve it:
-
Experience: Added in 2022, this refers to first-hand involvement with the topic. A review written by someone who actually used a product is more valuable than one based only on specs. Show experience through personal insights, real-world examples, or case studies. Phrases like “In my 10 years doing X…” signal authenticity.
-
Expertise: This is the depth of knowledge you or your author bring to the topic. Highlight credentials in author bios, cite reputable sources, and have content written or reviewed by subject-matter experts. Even if you’re not in a YMYL (Your Money or Your Life) field, demonstrating expertise builds trust and authority.
-
Authoritativeness: This is your reputation in the space. Are others referencing or linking to your content? Do you have a recognized brand in your niche? On-site, build authority with topic clusters and comprehensive content. Off-site, earn backlinks, contribute to relevant forums or media, and maintain an active online presence.
-
Trustworthiness: This is the most important of the four. Google wants to surface content from sites it can trust. Ensure your content is accurate and up-to-date. For more on how we help clients build trust and authority through design, see our accessibility compliance services. Be transparent — show contact information, secure your site with HTTPS, and clearly state policies (returns, privacy, etc.). Avoid broken links, low-quality ads, or anything that looks shady.
Bringing it all together, think of E-E-A-T as holistic SEO. It’s not just about one page or one technical tweak; it’s about the overall perception of your site’s quality. As an SEO specialist, I encourage clients to view E-E-A-T improvements not simply as tasks for better rankings, but as best practices for running a reputable online presence. When you focus on creating genuinely helpful content (Expertise + Experience), present it in a way that highlights your credibility (Authority), and run your site transparently and securely (Trust), you’re doing the right thing for users. Google’s algorithm updates increasingly aim to reward exactly that kind of website.
Take a moment to audit your site through the E-E-A-T lens. Do you demonstrate first-hand experience? Is your expertise clear and backed up? Are you building authority through content and references? Can a user trust your site with their data or trust the advice you’re giving? If you see gaps, prioritize filling them. It might be as straightforward as adding author bios, or as involved as a content overhaul with expert contributors – but any step toward higher E-E-A-T is a step toward better SEO resilience in 2025 and beyond.
Pro tip: You can even publish a brief author page for yourself (or your key content creators) highlighting qualifications and experience in the field. Not only does this boost E-E-A-T, but it can also personally connect with readers. On our own agency blog, I share my background and some of the results I’ve achieved for clients. This isn’t bragging – it’s establishing that when I talk about SEO, I do so with years of hands-on experience behind me. Don’t be shy about proving you know your stuff.
Conclusion: Stay Ahead in 2025’s Search Landscape
SEO in 2025 may feel complex — AI snippets, voice search, new metrics — but the core remains unchanged: connect people with what they need through useful, accessible content.
Let’s recap the key strategies:
- Understand and serve search intent: Go beyond keywords to deliver content that directly addresses what users want.
- Optimize for AI-driven results: Use structured content and concise answers to earn placement in featured snippets and AI summaries.
- Prioritize mobile-first and user experience: Make your site responsive, readable, and fast on all devices — especially mobile.
- Maintain technical SEO health: Regularly audit your site to fix broken links, duplicate tags, and crawling/indexing issues.
- Improve Core Web Vitals: Speed, stability, and responsiveness are key — not just for rankings, but for user satisfaction.
- Target long-tail and voice search: Think conversationally. Provide clear answers to niche and spoken queries.
- Boost E-E-A-T: Demonstrate your experience, back it with expertise, build authority, and earn user trust.
If this feels like a lot, you’re not alone. SEO is multifaceted, and no one has it all mastered. The key is to take a methodical approach: audit your current performance, identify gaps, and work through them one by one.
Whether it’s reworking your content to match voice search, speeding up your site, or highlighting your credentials for E-E-A-T — every improvement helps.
And if you’d like support, don’t hesitate to reach out. At Thursday Creative, we live and breathe SEO. We’d be happy to audit your site, offer advice, or roll up our sleeves and help implement these strategies with you.
Want to explore more SEO topics like this one? Browse our blog for expert strategies.
Change is constant in search. But with the right mindset — one that prioritizes people first — you can thrive in 2025 and beyond.
⸻
SEO in 2025 FAQ (People Also Ask)
Q: Is SEO still relevant in 2025?
Absolutely. SEO is just as relevant – if not more so – in 2025. While the methods have evolved (focusing more on intent, user experience, and content quality), the core goal remains: making your website visible to people who are searching online. As long as people use search engines to find information or services, optimizing for search will be critical. In fact, with increasing competition and new search features, a solid SEO strategy is often the deciding factor for whether your site gets noticed or not.
Q: How are AI-driven search results changing SEO?
AI-driven results (like Google’s AI summaries or answer boxes) are changing SEO by rewarding content that is structured and informative enough to be pulled into those answers. Websites now have to optimize not just for traditional blue links, but also for featured snippets and voice answers. This means writing clear, concise answers to common questions and structuring your content with headings and lists. SEO isn’t going away because of AI – instead, AI is forcing SEO to become more focused on quality content and direct answers. It’s an opportunity: if your content is the one chosen for an AI summary, you gain huge visibility (even if the click-through may not always follow).
Q: What is E-E-A-T in SEO?
E-E-A-T stands for Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness. It’s a set of criteria Google uses (especially in its quality guidelines) to evaluate how credible and reliable content is. Experience refers to first-hand experience on the topic, Expertise is the depth of knowledge, Authoritativeness is your reputation in the field, and Trustworthiness measures how honest and transparent your site is. For SEO, ensuring high E-E-A-T means creating content that is accurate, written by (or reviewed by) experts, and presented on a site that appears legitimate and trustworthy. High E-E-A-T can improve your rankings, particularly for sensitive topics like health, finance, or legal advice where Google is very careful about surfacing trustworthy information.
Q: Should I optimize for voice search?
Yes, it’s a good idea to account for voice search in your SEO strategy. Voice queries are becoming common thanks to smartphones and smart speakers. They tend to be longer and often phrased as questions or natural language requests. To optimize for voice, make sure your content includes conversational phrases and directly answers questions your audience might ask. It also helps to have an FAQ section or Q&A content that aligns with voice queries. Additionally, if you serve a local market, optimizing for voice search is a must – many voice searches are local (for example, “find a [service] near me”). By optimizing for voice, you’re also improving usability for all users, because you’re focusing on clear language and answering needs directly.
Q: What are Core Web Vitals and why do they matter for SEO?
Core Web Vitals are a set of three performance metrics Google uses to gauge user experience: LCP (Largest Contentful Paint) measures loading speed, INP (Interaction to Next Paint) measures interactivity responsiveness (replacing the older First Input Delay), and CLS (Cumulative Layout Shift) measures visual stability. These metrics matter because Google has made page experience a ranking factor – sites that load quickly and smoothly are favored. In practice, if your website provides a faster and more stable experience than a competitor’s, it could rank higher, all else being equal. Beyond rankings, Core Web Vitals are important because they directly affect how users perceive your site. A fast, responsive site keeps visitors around longer and reduces bounce rates. In summary, improving Core Web Vitals can boost your SEO and make your users happier – a double win in 2025’s competitive landscape.
Sources: